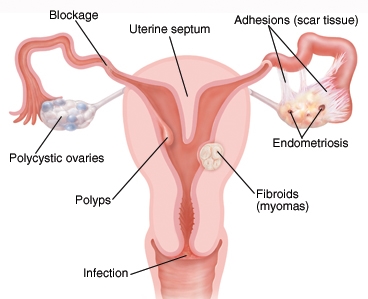
The uterus or womb is the organ of pregnancy and the largest of the organs of the female reproductive system of most mammals, including women. In addition, if it fulfills its function of welcoming the fetus until the end of pregnancy, the uterus greatly increases its size.
It is a muscular organ, hollow, pear-shaped, extraperitoneal, located in the woman's pelvis, between the vagina and the fallopian tubes.
In women of childbearing age, the ovaries produce the hormone estrogen at the beginning of the menstrual cycle. Estrogen helps prepare the lining of the uterus (called endometrium) for a pregnancy. When the uterus is ready, one of the ovaries releases an egg that goes down the fallopian tube, where it expects possible fertilization.
If the woman becomes pregnant, the already fertilized egg moves to the uterus, where it adheres to the endometrium. If you do not get pregnant, the endometrium and the unfertilized egg are removed through the vagina during the woman's next period.
AdvertisingProblems affecting the uterus
Some of the problems that can affect the uterus They are:
Non-cancerous masses in the uterus, called uterine fibroids, fibroids or fibroids, which can cause pain and bleeding, as well as complications in pregnancy. They are made up of muscle cells and other tissues that grow in and around the wall of the uterus. They are the most common non-cancerous tumors in women of childbearing age. This mass that is installed in the uterus can be from a centimeter in diameter to a couple of kilos of weight, be one or several, and sometimes do not cause any symptoms, which does not favor its detection. If they do, they usually consist of heaviness under the belly and pain in the pelvic area, vaginal bleeding for no apparent reason, discomfort in urination and during sexual intercourse, and abnormal abdominal enlargement.
Endometriosis, in which the lining of the uterus (endometrium) grows outside it, and affects other areas of the body (ovaries, fallopian tubes, large intestine and ligaments that support the uterus), causing in many cases fertility problems It can cause abnormal bleeding, dysmenorrhea and general pelvic pain.
In the adenomyosis, the tissue that lines the uterus grows on the outer walls of the uterus. Adenomyosis is a benign disorder is common in women who have given birth between the ages of 35 and 50 years of age. It is capable of producing painful periods (dysmenorrhea) or profuse (menorrhagia).
Hormonal imbalances that can cause painful uterine contractions or intense, irregular and painful menstrual periods.
Endometrial hyperplasia is a disease in which the lining of the uterus becomes too thick and causes abnormal bleeding. It is believed that hyperplasia is caused by too much estrogen.
Abnormal bleeding, which may be symptoms of various diseases. If you have uterine disease, the first sign may be a bleeding between periods or after sexual intercourse. Causes of abnormal bleeding include some of the problems discussed: hormones, thyroid problems, fibroids, polyps, cancer, infections or pregnancy.
Pelvic pain Without apparent cause it can also be an indicator of a problem in the uterus.
If you suspect any problem, you should see a doctor to make the correct diagnosis and be particularly informed of the possible treatments, since these will depend on the cause.
Whatever it is the problem that affects the uterus, we must bear in mind that every woman is different and that every medical case is different, and in many cases fertility problems can be overcome.